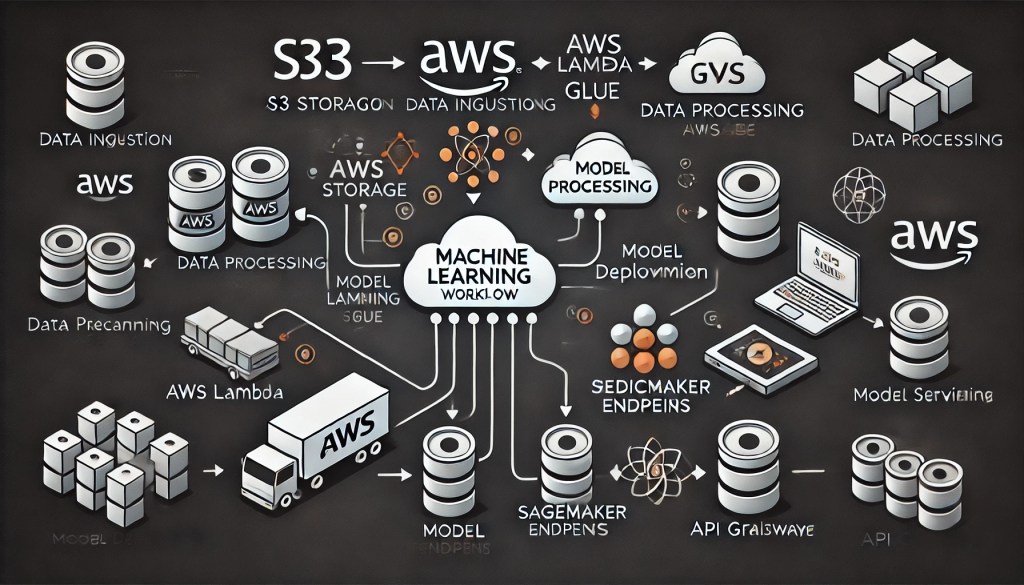
In today’s data-driven world, machine learning (ML) has transcended academic research to become a cornerstone of business innovation. From predicting customer churn to forecasting equipment failures, ML empowers organizations to make proactive, data-backed decisions. Amazon Web Services (AWS) stands at the forefront of this revolution, offering a suite of tools that streamline the end-to-end ML workflow. In this blog, we’ll dissect the lifecycle of a real-life ML prediction application, using AWS services to illustrate how businesses can deploy scalable, robust, and cost-effective solutions.
1. The Cornerstone: Defining the Problem and Gathering Requirements
Before diving into code, every ML project begins with a clear objective. For example, a retail company might aim to predict customer churn to retain high-value users. Key steps include:
- Stakeholder Alignment: Collaborate with business teams to define success metrics (e.g., reducing churn by 15%).
- Data Requirements: Identify data sources (e.g., transaction history, user engagement logs) and determine if real-time or batch processing is needed.
- AWS Services Involved:
- Amazon QuickSight for initial data exploration and visualization.
- AWS CloudFormation to provision infrastructure-as-code for scalability.
2. Data Collection and Storage: The Foundation of ML
Data is the fuel for ML models. AWS provides scalable storage solutions to handle diverse datasets:
- Amazon S3: A highly durable object storage service for raw data (e.g., CSV files, sensor logs). Use S3 buckets to organize data by project or date.
- Amazon Kinesis: For real-time data streaming (e.g., IoT sensor data or social media feeds).
- AWS Glue: A managed ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) service to catalog metadata and prepare data for analysis.
Example Workflow:
- Ingest customer interaction logs from a mobile app via Amazon Kinesis Data Streams.
- Store the raw data in an S3 bucket.
- Use AWS Glue Crawlers to auto-generate a schema and populate the Glue Data Catalog.
3. Data Preprocessing: Cleaning and Feature Engineering
Raw data is rarely ready for ML. AWS tools simplify preprocessing:
- Amazon SageMaker Processing: Run custom scripts (Python/R) to clean data, handle missing values, and engineer features.
- AWS Glue: Schedule ETL jobs to transform data into model-ready formats (e.g., Parquet).
- SageMaker Feature Store: Store and version features for reuse across models.
Pro Tip: Use SageMaker Processing to parallelize tasks on scalable compute instances (e.g., GPU-accelerated for image data).
4. Model Development: Training and Tuning
This stage is where ML magic happens. AWS offers tools for every skill level:
- Amazon SageMaker: A fully managed platform to build, train, and deploy models. Key features include:
- SageMaker Autopilot: Automatically trains and tunes models with zero code.
- Built-in Algorithms: Pre-configured algorithms for common tasks (e.g., XGBoost, Linear Learner).
- Framework Support: Integrate with TensorFlow, PyTorch, or Scikit-learn.
- Hyperparameter Optimization (HPO): Use SageMaker’s Hyperparameter Tuning to automate model optimization.
Example: To predict churn, train a gradient-boosted tree model on SageMaker, using customer demographics and purchase history. Run HPO to find the optimal learning rate and tree depth.
5. Model Deployment: From Lab to Production
A trained model is useless unless deployed. AWS enables seamless deployment:
- SageMaker Endpoints: Deploy models as real-time APIs. Scale endpoints automatically based on traffic.
- AWS Lambda: For serverless inference, trigger Lambda functions on new data (e.g., predict churn when a user logs in).
- Amazon API Gateway: Expose models as REST APIs for integration with web/mobile apps.
Cost Optimization: Use SageMaker Multi-Model Endpoints to host multiple models on a single instance, reducing infrastructure costs.
6. Monitoring and Maintenance: Ensuring Longevity
Models degrade over time due to data drift or concept drift. AWS tools help maintain performance:
- SageMaker Model Monitor: Detect data drift and model degradation by analyzing predictions vs. ground truth.
- Amazon CloudWatch: Track endpoint metrics (e.g., latency, error rates) and set alerts for anomalies.
- A/B Testing: Use SageMaker Canary Deployment to test new models against a subset of traffic.
Example: If Model Monitor detects a drop in accuracy, trigger a retraining pipeline via AWS Step Functions.
7. Iteration and Improvement: The ML Flywheel
ML is an iterative process. Use feedback loops to refine models:
- Amazon A2I (Augmented AI): Add human review to predictions (e.g., validate churn predictions with customer support input).
- SageMaker Pipelines: Build CI/CD pipelines to automate retraining with fresh data.
- Amazon Personalize: For recommendation systems, leverage pre-built workflows to improve user engagement.
8. Cost Optimization and Security: Best Practices
AWS offers tools to balance performance and cost:
- Spot Instances: Train models on discounted, unused EC2 capacity (up to 90% cost savings).
- S3 Intelligent-Tiering: Automatically move data between storage classes to minimize costs.
- Security: Encrypt data at rest (S3) and in transit (TLS). Use IAM roles to control access to ML resources.
9. Real-World Use Case: Predicting Equipment Failures in Manufacturing
Let’s walk through a scenario:
- Data Collection: Ingest sensor data from factory machines into Amazon Kinesis.
- Preprocessing: Use SageMaker Processing to normalize sensor readings and flag anomalies.
- Model Training: Train a time-series forecasting model (e.g., DeepAR) on SageMaker to predict failures.
- Deployment: Deploy the model as a SageMaker endpoint integrated with a maintenance dashboard.
- Monitoring: Use Model Monitor to track prediction accuracy and trigger alerts for potential downtime.
10. Future Trends: Generative AI and Edge Computing
AWS continues to innovate:
- Amazon Bedrock: A foundation model service for generative AI applications (e.g., chatbots).
- AWS DeepLens: Deploy computer vision models at the edge for real-time inference (e.g., quality control in manufacturing).
Conclusion: Empowering Innovation with AWS
The journey from raw data to actionable predictions is no longer a herculean task. AWS’s integrated ecosystem—spanning storage, compute, and ML services—enables organizations to deploy ML applications faster and more efficiently than ever. By leveraging tools like SageMaker, S3, and Glue, businesses can focus on solving real-world problems rather than wrestling with infrastructure.
As ML continues to evolve, AWS remains a trusted partner, offering scalable solutions for today’s challenges and tomorrow’s opportunities.
Ready to build your ML application? Start with a free tier AWS account and explore SageMaker’s interactive tutorials.
Scaling Your AI and ML Applications with AWS: A Practical Guide
Amazon Machine Learning Documentation
Overview of AWS Machine Learning Services
The Complete Guide to Machine Learning on AWS SageMaker
Machine Learning with AWS Services: A Comprehensive Guide
Top 15 AWS Machine Learning Tools in the Cloud Market

Leave a comment